
Media of Critical Care & Internal Medicine
What are symptoms of thyroid nodule
- Thyroid nodules are lumps that form within thyroid gland , it is a small gland located at the front of neck.
- Most of the thyroid nodules aren’t serious and don’t cause symptoms. Only a small percentage of thyroid nodules are thyroid cancer.
- Some thyroid nodules is visible in the neck as lump/swelling at front of neck
- Causes pressure symptoms such as difficulty in swallowing or breathing or change in voice.
Causes of Thyroid nodule
Reasons to develop nodules in thyroid gland:
- Iodine deficiency
- Overgrowth of normal thyroid tissue
- Thyroid cyst
- Chronic inflammation of the thyroid (thyroiditis). Hashimoto’s disease
- Multinodular goiter
- Thyroid cancer
Complications of thyroid nodule
- Difficulty in swallowing or breathing. Large nodules or a multinodular goiter can cause difficulty in swallowing or breathing.
- Hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism can result in weight loss, muscle weakness, heat intolerance, and anxiousness or irritability.
- Hypothyroidism, such as a slow heartbeat, dry skin, hair fall, weight gain and facial swelling
Diagnosis of thyroid nodule
Thyroid specialist doctor’s while assessing any lump or nodule in neck aims to assess functions of the thyroid gland and to rule out any possibility of cancer.
- Physical exam. Thyroid nodule usually move up and down during swallowing.
- Blood tests-Thyroid function tests- to assess thyroid functions blood levels of hormones produced by thyroid gland, and TSH released by pituitary gland are tested. It may show normal functions, Hyperthyroidism OR hypothyroidism.
- Ultrasonography. Best to understand structure of thyroid gland and nodules.
- Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy. FNA biopsy helps to differentiate between benign and malignant thyroid nodules..
- Thyroid scan. hot nodules –nodule producing excess thyroid hormone are seen as hot nodules
Treatment of benign thyroid nodules
- Watchful waiting. If a biopsy report shows a benign thyroid nodule, thyroid specialist may advice watchful waiting with regular follow ups and thyroid function tests.
- Thyroid hormone therapy
- Treating nodules that cause hyperthyroidism
- Radioactive iodine.
- Anti-thyroid medications
- Surgery
- Surgery
Thyroid Surgery is the best treatment for thyroid nodules that are:
- Cancerous nodule
- Suspected to be cancerous
- Large nodule causing pressure symptoms Nodule
- A fluid-filled (cystic) nodule returns after being drained once or twice.
What are Types of Thyroid Surgery?
Thyroid Surgery is 3 types:
Total thyroidectomy: Entire thyroid gland may be removed for-
Near Total (Subtotal Thyroidectomy): thyroid surgeon removes one lobe, isthmus and part of other lobe of thyroid.
Thyroid Lobectomy: Hemi Thyroidectomy
Normal lifeis expected after thyroid surgery, once you recover from the effects of surgery. Many patients become hypothyroid after surgery so thyroid hormone is given lifelong.
Get Consultation for thyroid surgery from our thyroid specialist at GB Multicare Hospital Nagpur- at 9823775733 online enqiry or Book appointment
Top 10 Ways To Prevent Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B (HBV) remains one of the leading cause of chronic liver disease mainly in South East Asia. Hepatitis B infection is caused by a virus that infects the liver and causes acute hepatitis (short-term infection) and chronic hepatitis B (long-term infection). Hepatitis B (HBV) damages your liver slowly (liver cirrhosis) and may lead to liver cancer. If you have hepatitis, you do not know it because nearly all chronic hepatitis B patients do not have symptoms. But as long as you have the virus, you can spread it to others and may damage your liver slowly.
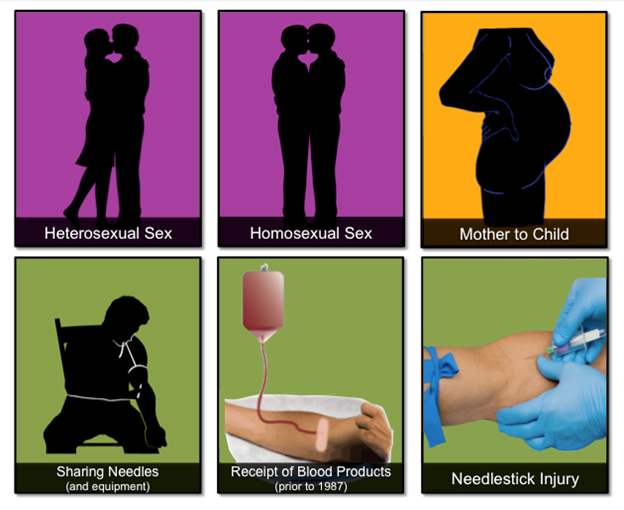
How does hepatitis B spread?

Though hepatitis B is a slow disease, yet you can prevent it by protecting yourself against it; the following top 10 preventive measures will help you:

- The best way to prevent hepatitis B is vaccination. The vaccine is given in a series of 3 to 4 doses. Ensure that babies, children, teenagers and adults should get vaccinated.
- Ensure that new born babies must get the hepatitis B vaccine at birth; infants should get all three shots by age 6 months. Health care workers and those who live with someone who has hepatitis B should get the vaccine.
- Infants born to mothers who have acute hepatitis B or have had the infection in the past should get a special hepatitis B vaccine within 12 hours of birth.
- Hepatitis B vaccine (HBIG) shot helps prevent infection if given within 24 hours of contact with the virus.
- Don’t share toothbrushes, nail clippers, or razors with an infected person. Little cuts in the skin while clipping nails, removing hair, or brushing teeth are perfect openings for viruses like hepatitis B to spread.
- Use condoms when you have sex. Well, lubricated latex condoms help prevents the spread of hepatitis B.
- Infinitesimally small drop of blood is enough to spread hepatitis B virus. Therefore, ensure that the needles used for piercing (tattooing) are properly clean & sterile.
- Ensure that pregnant woman must get tested for the virus.
- The blood used for transfusion should be screened for hepatitis B.
- Wear latex or plastic gloves if you have to touch blood.
Personnel working in police, fire department and paramedics should consider vaccination mandatory as they may accidently come in contact with the blood of accident victims. If you are already tested positive for hepatitis B, your liver function should be measured regularly to decide whether you need treatment and all the other members of your house should get vaccinated. Consult a hepatologist for further details and advice.
Join us in preventing hepatitis B by promoting awareness about it through campaigns and preventing it through vaccination.
