Media of Oncology & Onco Surgery
Diagnosis of colorectal cancer (Warning symptoms)
Cancer of the colon or rectum is more common after the age of 50 years.
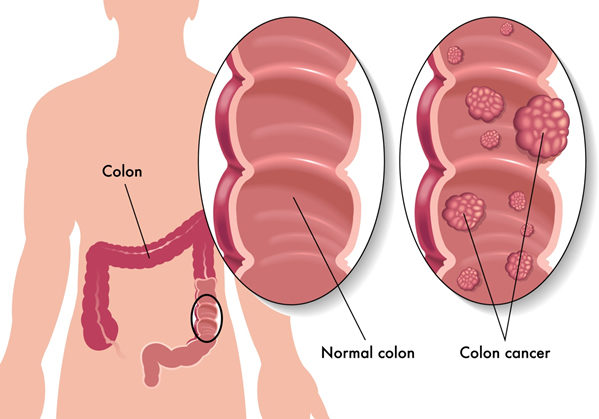
Colorectal Cancer is one of the cancers which can be prevented easily because it usually develops from polyps and POLYPS can be diagnosed early and can be removed before it changes to cancer.
Warning symptom of colorectal cancer–
- Blood in the stools
- Change in bowel habits
- Unexplained Anemia
- Unexplained abdominal pain
- Abdominal/rectal masses
BUT Colorectal cancer can be a silent disease and not have any symptoms at all.
Barium enema, CT colonography or CT scan May give the clue.
Diagnosis of colorectal cancer is confirmed by colonoscopy (endoscopic examination of large bowel) and biopsy.
Causes of Colorectal Cancer
Exact reason of colorectal cancer is not known, it is usually combination of genetic and environmental causes.
Approx 90% of environmental reasons are due to diet such as high calorie intake, red meat consumption, longer cooking times producing a higher concentration of carcinogens.
Other factors are obesity (though reason of why obese has more risk of colorectal cancer is not clear) alcohol and tobacco.
Prevention of risk of colorectal cancer
- The best way to reduce the risk is regular colorectal cancer screening
- Regular Exercise
- Diet rich in vegetables, fruits and high-fiber
- Avoid high fat foods.
- Moderate carbohydrate intake and reduce refined sugar intake
- Avoid smoking and moderate alcohol intake
- There is no clear evidence to support ‘antioxidants’, colonic irrigation or herbal remedies in prevention of colorectal cancer.
Screening for colorectal cancer
If you answer “yes” to any of the following questions, visit your colorectal or general surgeon about colorectal cancer screening-
- Are you aged 50 or older?
- Are you having blood in stool?
- Is there any recent change in your bowel habit?
- Has your first degree relative had colorectal cancer?
- Has your first degree relative had colon polyps?
- Do you have a chronic inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease?
colorectal cancer Screening schedule as per risk
Average Risk Group – Asymptomatic and no family history
- Screening starts at 50 years of age
- Digital rectal examination, and Stool occult blood testing – Every year
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy- every 5 years
- Colonoscopy – every 10 years
- Barium enema – every 5-10 years
High Risk Group
Family history of colorectal cancer- colonoscopy 10 years prior to youngest case in family
Personal history of colorectal polyp- Colonoscopy one year after polypectomy if polyp was more than 1 cm, multiple and villous or three years after polypectomy for solitary tubular polyp.
Personal history of colorectal cancer or endometrial cancer or ovarian cancer – Colonoscopy one year after resection
Very High Risk Group
Family history of familial adenomatous polyposis- Flexible sigmoidoscopy from puberty
Family history of non polyposis colorectal cancer- Colonoscopy 10 years prior to youngest family member
People with inflammatory bowel disease- after15th year of diagnosis
colorectal cancer Screening methods
Fecal occult blood testing (FOBT)
Flexible sigmoidoscopy:
Colonoscopy
Other screening tests i.e. barium enema, and CT colography (virtual colonoscopy) may not be as effective and reliable as FOBT or colonoscopy
Breast tumor /LUMP in Breast
During self-examination of breast for Breast cancer screening , you find a swelling or lump in breast and you are scared… what to do next?
Don’t panic as most breast lump are benign ie not cancer, however it can be sign of breast cancer so visit a general surgeon immediately to investigate it further and take proper treatment.
Breast lumps are often painless, though some may be painful. Reason for breast pain is usually hormonal variations related to menstrual cycle and pregnancy. Hormonal medications, including some infertility treatments and oral birth control pills may also cause breast pain.
Causes of Breast Lump
- Fibrocystic changes: Due to hormonal changes in menstrual cycle and are hard or rubbery. There may be pain on pressing breast lump.
- Fibroadenoma: It is most common type of breast lump and on touch it is rubbery , round and usually there is no pain
- Mastitis: infection in breast tissue may cause painful lump.
- Breast Cancer: Intraductal papilloma, Breast cyst, Lipoma, injury (trauma to breast) may also cause breast lump.
Tests to Diagnose a Breast Lump
After through Clinical examination, specialist may advise following tests:
- Mamogram
- Ultrasound
- MRI
- Fine needle aspiration
- Biopsy
Treatment of Breast Lump at Nagpur
First step to plan proper treatment for breast lump is diagnosis and determine the cause of breast lump.
Fibrocystic breast changes do not require any treatment as it goes after menstrual cycle is finished. But to relieve pain treatment may be recommended.
Simple cyst can be treated by aspirating the fluid by a small needle. After aspiration usually cyst disappears by its own.
Fibroadenoma and intraductual papilloma are removed by surgery.
Abscess or Infection in breast requires antibiotics.
Breast Cancer Treatment Includes:
- Removal of the lump
- Removal of the breast
- chemotherapy
- radiation Therapy
- Hormone therapy
Risk Factors for Breast Cancer
The following are risk factors are strongly related to the higher chances of developing breast cancer:
- Breast cancer in family more so if they had it before age of 50 year
- In general, the older you are, the greater your risk
- A history of benign breast disease
- Other breast conditions: lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) or atypical hyperplasia
- Radiation therapy to chest before age of 30 is at increased risk of breast cancer
- Certain genome changes: Changes in certain genes, such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, substantially increase the risk of breast cancer
- No pregnancy or late first pregnancy (first child after age 30)
- Early menarche: First menstrual period at an early age before 12
- Late menopause after 55 years of age
- Overweight or obese after menopause
- Lack of physical activity
- Drinking alcohol
Symptoms indicating that a Breast Lump Could be Breast Cancer
- Lump or thickening of the breast
- Dimpling or puckering of the skin
- Change In skin color of the breast or its texture
- Change in breast shape
- Swelling, redness or heat in the breast
- Discharge from the nipple
- Retraction of the nipple
Breast lump can occur in both male and female and a visit to specialist doctor is required to diagnose it properly. Depending upon the type of breast lump a suitable treatment is planned.
Fibre: Your Savior Against Irritable Bowel Syndrome (Ibs), Colon Cancer And Diverticulosis

IBS is one of the most common disorders of the lower digestive tract that results in altered bowel habits – bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, and diarrhea. IBS attack is often triggered by poor dietary habits, certain medications, anxiety and emotional tension. Never ignore constipation because, if left untreated, it may lead to diverticulosis of the colon. But, don’t worry,
Whatever may be the reasons for your IBS, fibre is your savior – let us find out how!

Do you know: Fibre in diet may help reduce Colon Polyps and colon Cancer?
Colon cancer can be prevented provided you should monitor your diet. According to several research studies unprocessed grains are vital in preventing colon cancers – the reason: fibre in high concentrations in the diet makes the stool bulky, smooth and helps in removing carcinogens from the walls of the colon quickly. Less carcinogenic exposure to the colon may mean fewer colon polyps and hence less chances of cancer.

Fibre and Diverticulitis: is there any link?
Diverticulosis is a condition in which prolonged, vigorous contractions of the colon in the left lower side causes increased pressure that eventually results in the formation of ballooning pockets. These pockets don’t cause any problem, but may become break open or infected causing infection or inflammation. A high-fibre diet may increase the bulk in the stool and thereby reduce the pressure within the colon. By doing so, the formation of pockets is reduced or possibly even stopped.
Is dietary fibre supplement helpful?
If you can’t tolerate enough fibre in your diet, then stool softening and bulking agents are available. These agents absorb water and add bulk to the stools Therefore; they are useful in preventing and treating digestive tract disorders. These contain psyllium mucilloid and come from the seed of the psyllium plant. Citrucel (hemicellulose) and FibreCon (polycarboxisal) are other bulking agents that can also be used.
What are the food sources of dietary fibre?
The foods that are rich in dietary fibre are the following:
- Cereals, whole bread and Oat bran
- Fresh fruits
- Dried or stewed fruits (prunes, raisins or apricots)
- Fresh vegetable
What additional measures will you take to prevent IBS?
Try to adopt the following rules:
Drink plenty of liquids, eat bran cereals in the morning (oat bran, raisin bran, and oatmeal are some of the high-fibre cereals. Eat slowly and chew your food thoroughly – this will help the food to break easily in the mouth and stomach with saliva and digestive juices, respectively. It may also help prevent problems from developing in the lower digestive tract.
Eat your meals at regular intervals. Eat fruits on a regular basis; in fact, making fruit a part of daily meal prevents lots of digestive issues. Fruit juices on the other side do not help in these digestive issues because fruit when eaten wholesome only adds fibre to the diet.
Increased amounts of fibre in the diet can help relieve the symptoms of IBS by producing soft, bulky stools and thus prevents you from diverticulosis and colon cancers. This helps to normalize the time it takes for the stool to pass through the colon. Liquids help to soften the stool – the end result no constipation, no abdominal pain and eventually no IBS.
A Few Faqs On Liver Health And Liver Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a liver disease accompanied with an abnormal structure & function of the liver due to damage caused to the liver cells, which results in the death of the liver cells and formation of scars. The slow progress of liver cirrhosis if left unchecked, may lead to life-threatening complications of the liver and impact your overall health, but the information given below will help you to know it on time and approach your gastroenterologist or hepatologist as early as possible to avoid future health complications. By the way, Protecting your liver will not only make you healthier today but will ensure that that you have a healthier tomorrow.
here are a few questions that i get asked by my patients on a day to day basis:
What is the function of Liver in our body?
The liver carries out several necessary functions, including detoxification of harmful substances in your body including alcohol and drugs, cleaning your blood and making and storing some vital nutrients. Liver also Manufactures bile and helps in digestion, stores sugar in the form of glycogen, breaks down saturated fat and produces cholesterol.
What is Liver Cirrhosis?
In liver cirrhosis injury is caused to liver cells and they get killed. The injured liver cells start to repair; In the process, the inflammation and repair of the dying liver cells cause scar formation. Next, the liver cells that are alive multiply to replace the dead cells. This results in the formation of cluster of newly formed liver cells within the scar as shown in the figure. Cirrhosis is a liver disease accompanied with an abnormal structure & function of the liver. If unchecked it can even prove life-threatening.
Why You Get Liver Cirrhosis?
You get liver cirrhosis due to Hepatitis B & C disease, Alcohol abuse, Fatty Liver Disease associated with obesity & diabetes; viral Infections; blockage of the bile Duct; Heart attacks; accumulation of toxic metals: copper & iron in the liver due to genetic diseases; Certain medications, inherited disease like cystic fibrosis, prolonged exposure to environmental toxins, parasitic infections and autoimmune diseases.
What happens Due to Liver Cirrhosis?
In Liver cirrhosis as the association between liver cells and blood is lost, liver cells’ ability to add and or remove substances from the blood is also lost. The next problem is the disturbance of bile cells & bile channels – due to this toxic substances do not get removed, but accumulates altering the function of the liver and digestion because bile helps in both these functions. As a result of this scars form in the liver; detoxification of the toxins stops; the processing of nutrients, hormones and drugs stops; liver produces toxins.
What are the symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis?
The symptoms of the liver cirrhosis vary according to the stages of the disease. There are no symptoms in the beginning, but as the disease progresses, the symptoms include the following:
- Fever
- Bleeding occurs
- weight loss
- Fatigue
- Yellowing of the skin due to jaundice
- Itching
- Loss of appetite
- Fluid retention (edema) and swelling in the ankles, legs, andabdomen (often an early sign)
- Blood in the stool
- Light-colored Stools
What are the Possible Complications?
Coagulopathy – bleeding disorders
Bacterial Infections
Veins in the stomach, intestines and esophagus enlarge and bled easily
Kidney Failure
Liver Cancer
Increased pressure in the blood vessels of the liver (portal hypertension)
Mental confusion, change in the level of consciousness, or coma (hepatic encephalopathy)
Why Early detection of Cirrhosis is essential?
You must pay heed to this because liver damage due to cirrhosis can’t be replenished. Therefore, it is mandatory to diagnose cirrhosis early & treat it immediately to stop further liver damage. Moreover, cirrhosis is progressive and makes liver function more and more difficult. In the advanced stages, it could be life-threatening.
What Physical Examinations your doctor will do?
Your physician will look for swollen abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid and to detect enlarged spleen or liver; He will also look for red spider-like blood vessels on the skin and yellow eyes or skin (Jaundice).
What Tests Your Physician will recommend?
- Complete Blood Count
- Prothrombin time
- Liver function test
- Blood Albumin level
Other tests to check for liver damage include:
- Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen
- Endoscopy to check for abnormal veins in the esophagus or stomach
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
- A liver biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
How can I prevent Cirrhosis of the liver?
- Avoid synthetic chemicals
- Avoid unprotected sex
- Avoid alcohol
- Maintain healthy weight
- Adopt personal hygiene
- Eat Healthy Diet low in salt
- Get your vaccination done for Hepatitis B and A, pneumonia and influenza.
- Talk to your doctor about all medicines you take, including herbs and supplements and over-the-counter medicines.
It’s not only you, but most of us often think that liver disease is life-threatening.However, proper knowledge of the disease and timely consultation with a hepatologist defy such notion. The sooner you begin comprehensive risk reduction, the longer and stronger your liver will function and retain its proper structure. Your Lifestyle Changes, knowledge about the disease and on time approach to a hepatologist not only minimize the risks of liver Disease, but also protects your liver to ensure the healthiest and happiest life. It is the best defense against liver disease and, in fact, your responsibility.
Avoid Colorectal Cancer By Early Screening
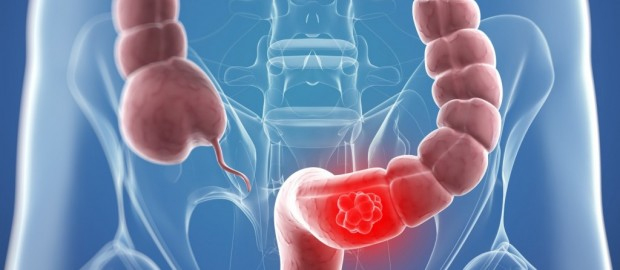
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in both males and females across the world. Majority of the cancers occur in individuals 40-69 years age, a peak age for economic productivity. Breast, cervical & colorectal cancers account for over 40% of the incidence of cancer cases in India. These cancers have highest cure rates if diagnosed in the early stages through screening. Let us learn how screening is beneficial to detect colorectal cancer in the beginning itself.
What is colorectal cancer?
The colon and rectum are part of the large intestine. Colorectal cancer is a term for cancer that develops in the colon & rectum (Abnormal growths in the colon or rectum). It initially starts as a polyp (a growth in the inner lining of colon or rectum), which in most of the cases is not cancer. Only a few polyps, called adenomas can develop as cancer (adenocarcinoma). However, if a polyp is taken early, when small, it may not become cancer. Over 95% of colon and rectal cancers are adenocarcinomas.
Why the mortality rate is high in cancer, particularly in India?
Lower rates of colorectal cancer screening contribute to increase the risk of CRC. Majority of cancers can be effectively treated with curative intent if diagnosed earlyand treated appropriately. However, in India, delayed diagnosis, poorly equipped hospitals coupled with sub-optimal therapy accounts for high cancer mortality compared to the Western and European countries.
Why screening is important?
Certain cancers like colorectal cancer has a pre-cancer stage called colon polyp, which is a small overgrowth of tissue in the form of a small grape like swelling – when these lesions are found and treated early, it is possible to prevent future cancer in an individual. Screening is the process of looking for cancer or pre-cancers (colon polyps) in people and finding them early. The polyps can be removed before they have the chance to turn into cancer.
Furthermore, you are more likely to get colorectal cancer, if you have colorectal polyps, a family history of colorectal cancer, ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, and if you eat a diet high in fat, or smoke. In view of the above facts, cancer screening is recommended to detect colorectal cancer early. Many people do not experience symptoms in the early stages of cancer. And thus, in the absence of any symptoms, screening helps detect cancer early when it is most treatable. When symptoms appear, they’ll likely vary, depending on the cancer’s size and location in your large intestine.
How is Colorectal Cancer screening done?
If your doctor suspects that you could have colon cancer, they may examine your colon using a scope: colonoscopy, wherein a long flexible tube attached with a camera & surgical tools is passed inside your colon to take tissue samples (biopsies) for analysis. Polyps can also be removed completely during a colonoscopy. The tissue samples are sent to the lab for further analysis. Even though other tests might suggest colorectal cancer, a biopsy is the only way to know for sure. Furthermore, your doctor may do blood test including liver function test to know whether the cancer has spread to the liver.
Next, your doctor will order tests to determine the stage of the cancer, which will help determine the most appropriate treatment for you. The staging tests include Computed tomography (CT or CAT scans) to know the extent of cancer spread to liver, lungs or other organs of the body. CT scans can also be used to guide a biopsy needle into a tumor. Other tests include Ultrasound, MRI scans, chest X-ray, and PET scans.
What is the treatment?
The type of treatment your doctor recommends will largely depend on the stage of your cancer. The treatment includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation or a combination of all. Surgery can usually cure it when it is found early. With early detection, by surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy colorectal cancer can be effectively treated. Therefore, gastroenterologists and cancer specialists recommend colon cancer screening (colonoscopy) for everyone over age 50. Tests to detect blood in stool are also recommended. If you have any familial history, you may need frequent screening programs. If you’re concerned about your family’s history of colon cancer, talk to your doctor about whether your family history suggests you have a risk of these conditions.
Minimally Invasive Surgery For Cancer: The Best Alternative To Open Surgery
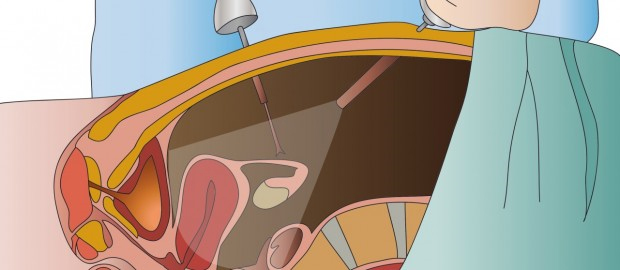
Minimally invasive surgery is a boon for patients as well as surgeons. It is also known as endoscopic or key-hole surgery. It is a very effective approach for removing some cancerous tumors and lymph nodes – all the while sparing the patient from tissue damage, pain and scarring. In other words, MIS is redefining the surgical approach; let us understand why MIS is good for cancer.
What is Minimally Invasive Surgery?
In traditional surgery, a surgeon needs to make a large incision in order to operate. With MIS, the surgeon makes a few small holes that are usually less than 1/2 an inch. The surgeon then inserts specially designed, thin instruments and sophisticated video equipment to perform the operation through the small opening.
Laparoscopic surgery means key-hole surgery of the abdomen. This is used to diagnose and treat many types of cancer–including gastrointestinal, uterine, cervical, kidney and urinary bladder cancers.
Thoracoscopic surgery or video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) means a key-hole surgery in the chest. This is used for treating lung & esophagus (food pipe) cancers.
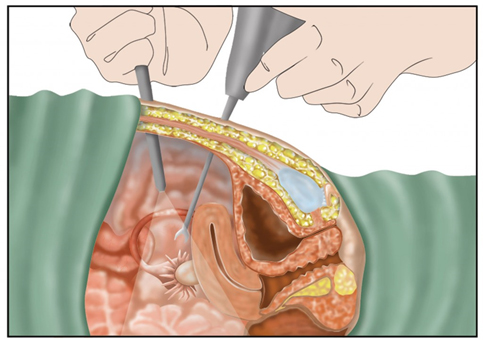
Is minimally invasive surgery safe?
Every surgical procedure, whether minimally invasive or traditional, carries some sort of risk and complications. Minimally invasive surgery has been thoroughly studied in numerous clinical trials spanning across the world and, in general, the risk of complications is similar to that seen in traditional open surgery.
Can complex cancer surgeries be done as minimally invasive surgeries?
In the beginning when MIS was gradually gaining prominence, gynaecologists and surgeons used to perform MIS or laparoscopic surgery for relatively simple procedures. Gradually as the procedure started gaining wide acceptance – the popularity of laparoscopic surgery and development of newer devices for tissue dissection and better cameras for better visualization and better magnification led to the use of laparoscopic techniques for other procedures – including cancer surgeries. However, cancer surgeries are quite complex and extensive (demand precise dissection near blood vessels) – and therefore, require hands-on expertise and surgical skills and can only be done by a very few immensely experienced onosurgeons. Furthermore, better visualization and better magnification can help in precise identification & better clearance of cancer. Now, MIS done by experienced onco-surgeons has been accepted as a standard surgical procedure for cancers.
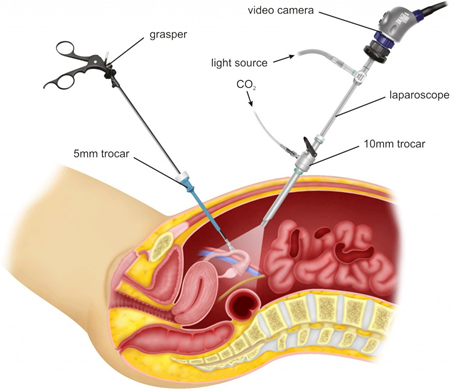
Advantages of Minimally Invasive Surgery
MIS procedures cause less post-operative pain and discomfort. Studies have shown that patients undergoing MIS procedures report less pain and require smaller doses of pain relievers. MIS procedures require a smaller incision – which means small, less noticeable scars. The other benefits of MIS include less blood loss, decreased need for blood transfusions, shorter hospitals stays, early resumption of regular diet, quick recovery and return to normal activities.
The bottom line is that MIS procedures use highly sophisticated cameras and video-assisted equipment thus ensuring a better visualization and better magnification of the internal organs and structures for the surgeons. And, for patients, MIS is a more accurate, less painful, precise and definitive procedure with better outcomes and cure rates.
